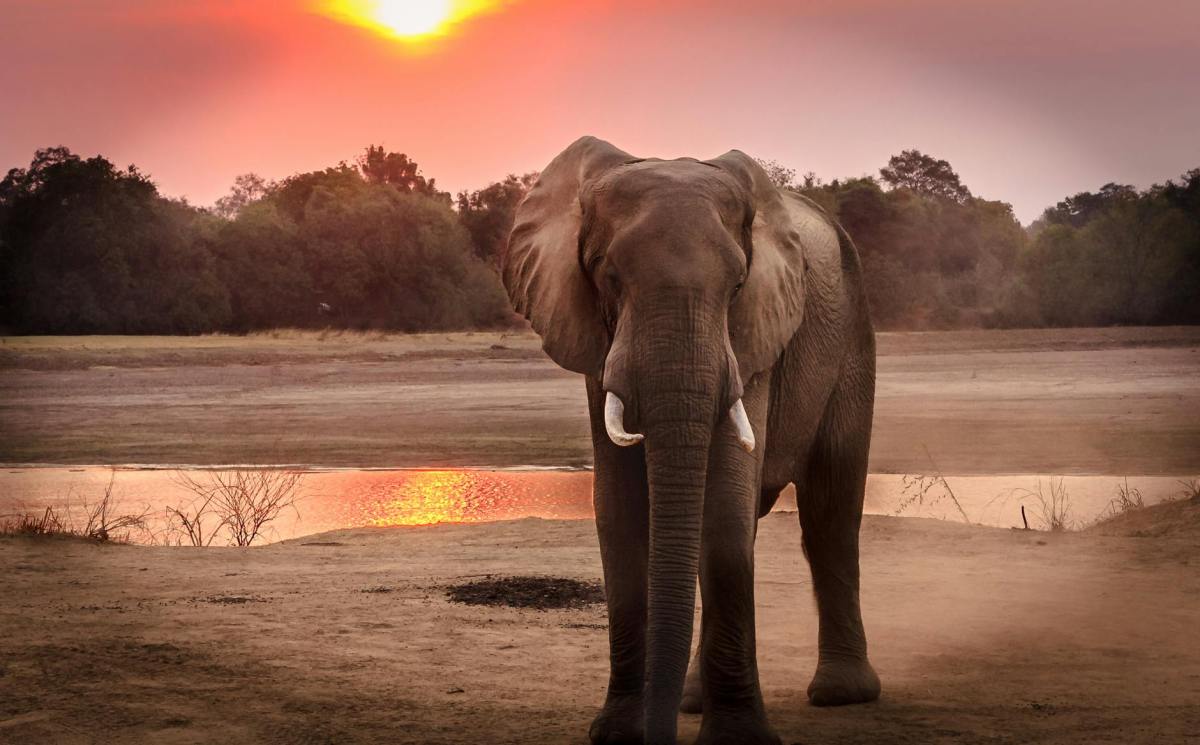
Elephants are famously social animals, moving in matriarchal herds that can consist of as many as 70 of their kind.
They also communicate over long distances, emitting rumbles that can be heard miles away.
Because of their social and nomadic existence, it makes sense that elephants would need a way to single out individuals and address each other, and for the first time researchers say they’ve found evidence of Earth’s largest land animals calling each other by name.
“If you’re looking after a large family, you’ve got to be able to say, ‘Hey, Virginia, get over here!’” Duke University ecologist Stuart Pimm told the Associated Press.
The research involved field work and analysis using artificial intelligence. To record samples of elephants communicating, teams followed herds with recording equipment. Notably, elephant rumbles include sounds in frequencies lower than the human ear can detect.

The team paid close attention when one elephant vocalized and another responded, and recorded who initiated each rumble and who it was meant for.
Although elephants are best known for making loud “trumpeting” sounds, experts say those are more like exclamations while rumbles contain encoded information that African savanna elephants would need to communicate to each other.
“The rumbles themselves are highly structurally variable,” said Mickey Pardo, a biologist from Cornell University and co-author of the study. “There’s quite a lot of variation in their acoustic structure.”
A machine learning algorithm was then used to sort and categorize the large number of audio samples, looking for patterns that are difficult for human minds to detect.
“Elephants are incredibly social, always talking and touching each other — this naming is probably one of the things that underpins their ability to communicate to individuals,” said George Wittemyer, an ecologist at Colorado State University and co-author of the study. “We just cracked open the door a bit to the elephant mind.”

Notably, the elephant “names” are identifiers that they created for themselves, and are not the kind of human-bestowed names that cats and dogs respond to. The list of animals who have names for themselves is short, although likely to expand with further study. Dolphins, for instance, identify themselves with unique whistling patterns, and parrots have a similar method, but both species address individuals by imitating their calls. Elephants use their name analogs the way humans do, to directly address each other.
The research has the potential to raise public awareness of elephant intelligence and their plight as they face threats to their continued existence. Like almost all of the Earth’s iconic megafauna, elephants will become extinct if we don’t do a better job protecting them and ending the ivory trade. Every year about 20,000 elephants are slaughtered for their tusks to feed the demand for ivory, especially in China where it’s considered a status symbol, according to the World Wildlife Fund.
Yang Feng Glan, known as the”Queen of Ivory,” was sentenced to 15 years in prison by a Tanzanian court in 2019. Yang smuggled some 860 elephant tusks worth $6.5 million from Tanzania to China as the leader of one of the world’s most extensive poaching and ivory smuggling organizations.
During her years operating the smuggling ring, Yang presented herself as a successful businesswoman and ran in elite circles within China, authorities said. Two of her accomplices were also given 15-year sentences for their roles, but since then others have filled the vacuum left by Fang’s conviction, and elephant preserves are constantly under threat from heavily armed poachers.