Jaguarundi
Taxonomic name: Herpailurus yagouaroundi
Genus: Felis (small cats)
Size: Males weigh up to 20 lbs, with typical sexual dimorphism for felid species
Lifespan: Up to 20 years in captivity
Gestation: 75 days
Litter size: Between one and four kittens per litter
Distribution: Almost the entirety of South America as well as the southern US
IUCN Red List status: Least concern, but threatened by habitat loss

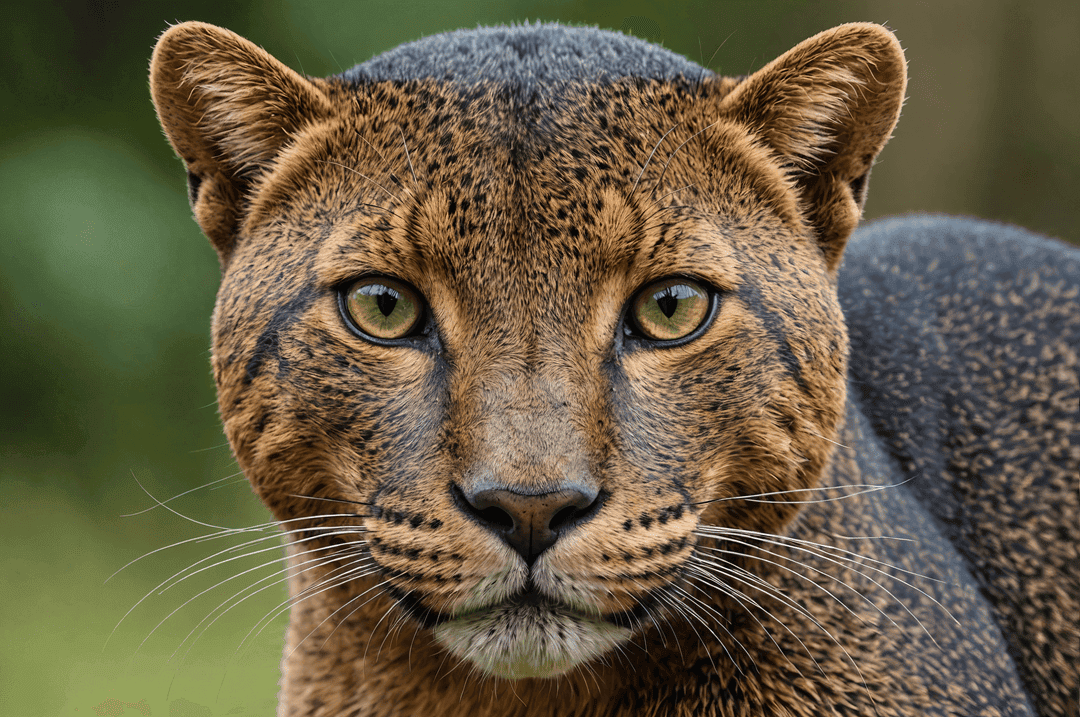
If you spot a jaguarundi in the wild, there’s a good chance you won’t know what you’re looking at.
Their sleek, elongated bodies are almost weaselesque when seen from the side, an impression made stronger by the way their heads are shaped in profile. From some angles they can strongly resemble otters, an likeness strengthened by their short, dusky coats.
But seen head-on they’re definitely cats, and even though they’re small felines — about one and a half to two times the size of domestic kitties — their facial features can be reminiscent of big cats, especially their broader noses, rounded ears and the set of their eyes.
Seen from an angle like this, jaguarundis resemble jaguar cubs:
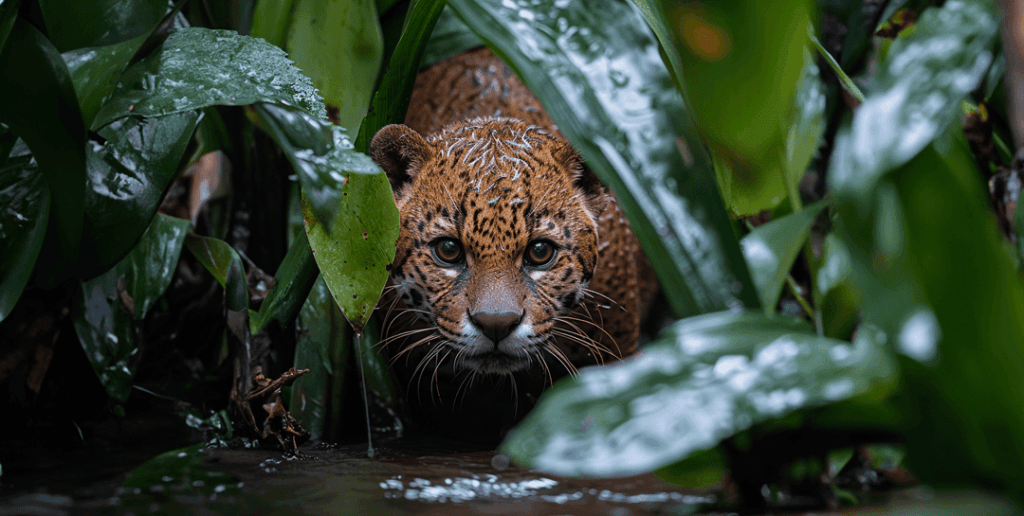

Indeed, jaguarundi means “dark jaguar” in Old Guarani, an extinct predecessor of the Tupi family of indigenous languages that were spoken in South America for thousands of years before the arrival of the conquistadors and the Spanish language. Modern variants of the language still exist in countries like Paraguay, which may account for the enduring names of several species of western hemisphere cats. (Jaguar itself is based on the indigenous Tupi word “yguara,” and pumas have dozens of surviving names with indigenous roots to go along with their many names in English.)
As New World cats, jaguarundis boast an impressive range that stretches from southern Argentina through Latin America and into the lower US states.
Like their larger cousins, the jaguars, jaguarundis are comfortable in the water and are strong swimmers. They’re also adept hunters on land, excellent climbers, and they’re impressively sure-footed while traversing branches high above ground level.
In short, the adaptable felines can just about do it all.
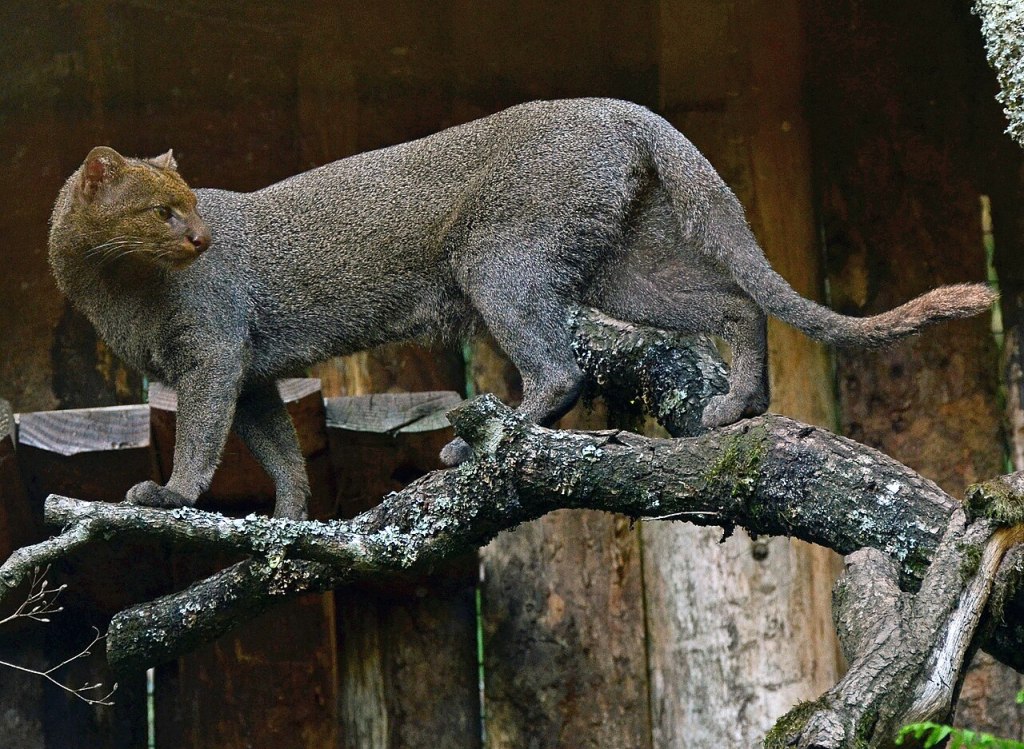

In the wild, jaguarundis have been known to hunt prey as large as small deer and help themselves to seafood snacks when the mood strikes them, but analyses of their diets shows they have a strong preference for mammals, particularly a variety of wild rodents found in dense jungles and forests.
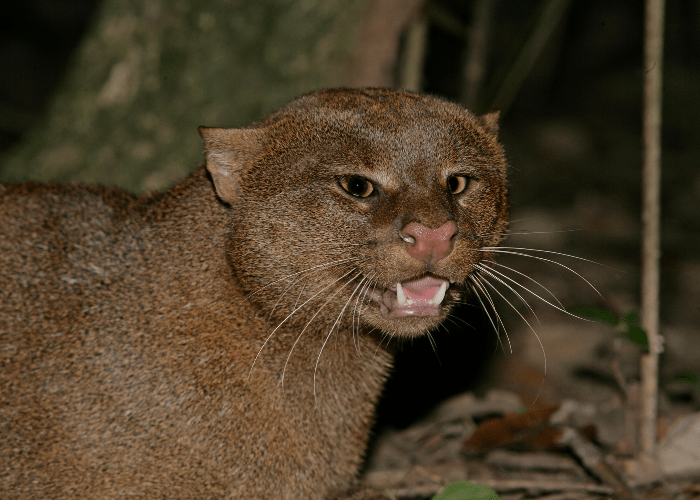

Jaguarundis don’t just look different compared to other cats — they sound different as well.
Conservationists call the jaguarundi’s vocalizations “whistles” and “chirps,” but to us they sound more like squeaks.
Take a listen for yourself:
It’s illegal under the Big Cat Public Safety Act to keep jaguarundis as pets, and the jaguarundi curl, a breed meant to mimic the appearance of the jaguarundi, is not related to the wild cat.
While they’re known to range in Texas and Arizona, sightings of jaguarundis are rare. From a distance their movement looks almost indistinguishable from those of house cats, and they’re famously elusive — by the time most people do a double take, the shy felines have disappeared into tall grass, brush or jungle.
Images via Wikimedia Commons
Previously:
Amazing Cats: The Mysterious Marbled Cat
Amazing Cats: The Rusty-Spotted Cat
Amazing Cats: ‘He Who Kills With One Bound’
Amazing Cats: The Puma
Amazing Cats: The Sunda Clouded Leopard
Amazing Cats: The Adorable Colocolo, Feline of the Pampas
Amazing Cats: The ‘Fire Tiger’ Is The Stuff Of Legend
Amazing Cats: Ocelots Love Trees, Water And Calvin Klein’s Obsession For Men
Amazing Cats: Pallas Cats Are The Grumpy Little Hobbits Of The Feline World