Whatcha want, whatcha wanna do? Whatcha gonna do when they come for you?
Two vicious criminals were caught by the long hand of the law and face justice for the community-destroying act of…trapping and feeding cats. The heroic police officers responsible for meting out justice were from the Wetumpka Police Department in Wetumpka, Alabama, about 20 miles north of Montgomery.
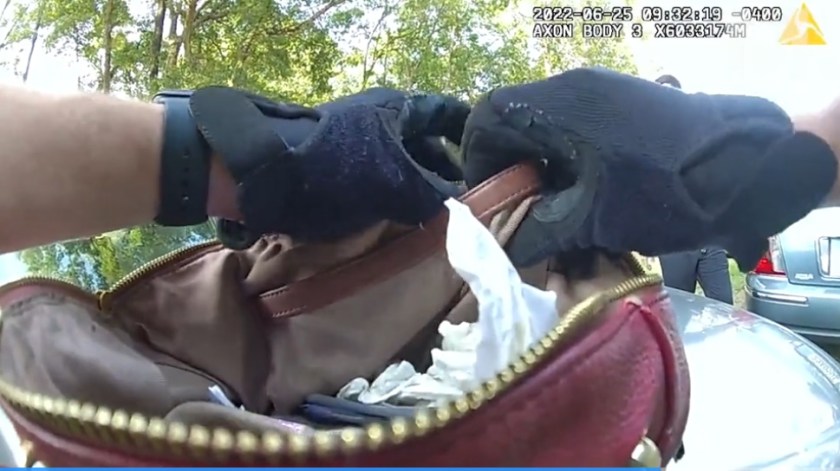
Fearless cops arrived at a public park on June 25 and immediately took up tactical positions after receiving intelligence that two seasoned criminals were trespassing on public land and defying the law by feeding the dangerous beasts. Even worse, the alleged lawbreakers were conducting their brazen activity in broad daylight!
After they were satisfied that 84-year-old Beverly Roberts and 60-year-old Mary Alston were not hiding weapons in the bags of cat food they’d brought with them, and could not repurpose their cat traps to harm officers, the intrepid lawmen courageously confronted the pair of malefactors, telling them to cease their illicit activity and vacate the premises.
The officers approached Alston first, warning her that she was breaking the law by feeding stray cats who were “becoming a nuisance.”
A flabbergasted Alston said she was trying to help the situation by trapping the cats and bringing them to shelters, pointing out she had a trap already deployed and had other trapping equipment in her car.
But the officers noted such specialized work is the domain of trained professionals — in this case the town’s absent animal control officer — and told her to leave.
“I’m teetering on going to jail for feeding cats?” the hardened alleged criminal asked, bristling with obvious disdain for authority.
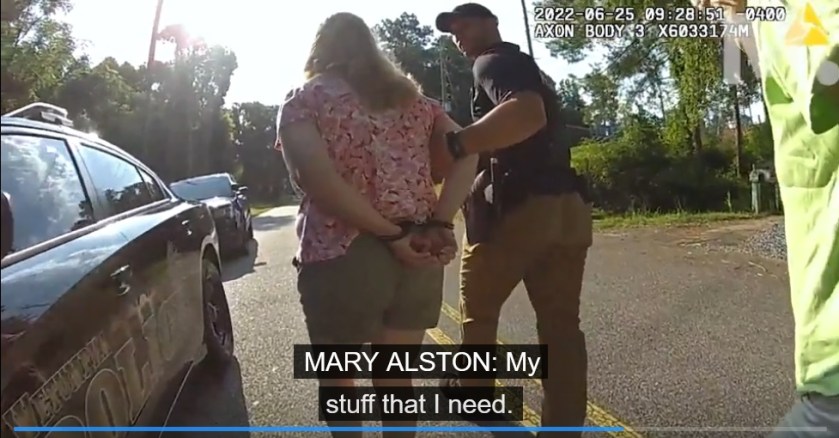
The clearly dangerous woman thought she could retrieve her traps and pack up her belongings, but the resolute police were having none of her defiant attitude.
“She’s still sittin’ here after we done told ’em to leave already,” an officer complained to a dispatcher during an aside filmed in his patrol car.
When Alston expressed surprise that police were cuffing her, the officers explained they had already emptied their vast reservoir of patience after telling her to leave the park.
“You aren’t doin’ it fast enough and now you’re going to jail!” an officer said after literally yanking Alston out of her driver’s seat with both hands. (An act completely justified, we’re sure. You don’t last long as a lawman in a depraved town like Wetumpka if you can’t quickly spot possible danger.)
Meanwhile, Roberts demonstrated clear contempt for authority when she questioned why an entire shift’s worth of cops were present, and went to hand her car keys to Alston before the officers arrested her. She explained she was handing off her car keys because she didn’t want the vehicle sitting in a public park unattended, not yet realizing the police would do her a favor by impounding her car.
“It’s gonna get ugly if you don’t stop!” one officer said, warning the incredibly dangerous woman, who further insulted the valorous public servants by questioning their use of time and resources on a cat-feeding complaint.

Knowing the 84-year-old could be deceptively strong, the officers cuffed her with her hands behind her back, then expressed skepticism when she couldn’t physically get into the back seat of a police SUV while restrained.
After both women were restrained and under control in the back of a patrol cruiser, the cops reflected on a tense situation that could have gone wrong at any moment.
“I’m glad nobody recorded, because [it’s] a bunch of police officers beatin’ up on a couple old ladies,” an officer said while another laughed off camera.

We here at Pain In The Bud commend the Wetumpka Police Department for showing no mercy to their town’s seasoned criminal element.
Recent examples of cowardice in high-profile policing situations (Uvalde, Texas, and Marjorie Stoneman Douglas High School in Florida) may have shaken the public’s confidence in our normally intrepid police, but the officers of Wetumpka valorously charged into this situation despite great risk to themselves, clearly understanding the immediate danger Alston and Roberts posed to the community with their allegedly law-breaking acts.
After righteously fighting attorneys for both women and refusing to release body and dash cam footage of the tense encounter, Wetumpka police could no longer drag their feet after three months of stalling and were finally forced to hand the video over due to clearly anti-American laws supposedly meant to guarantee “freedom of information.” Obviously, such laws were created to benefit cat-feeding terrorists and other dangerous criminals.
The attorneys believe the footage will vindicate their clients, but any reasonable person who views tape of the encounter will certainly come away with nothing but admiration for the police officers, who wisely prioritized using their resources on such a brazen and community-destroying crime.
The town of Watumpka, and all of America, owes a debt to these fine men.













