We know cats use non-verbal signals to communicate with each other, but recent research suggests we may just be scratching the surface, glimpsing only a portion of the information that passes between our furry friends.
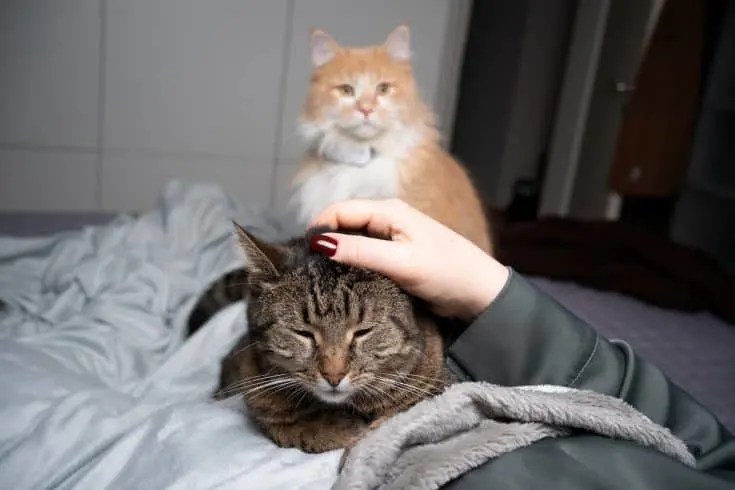
Cats “talk” to each other by the way they position their tails, whiskers and ears, in addition to their overall body language.
It turns out there’s more. A group of interdisciplinary scientists from universities in Kansas, Arkansas and Haifa, Israel, found cats also employ specific facial expressions, and rapidly mirror each other’s expressions during play time to signal they’ve got good intentions and aren’t going to hurt each other.
The study, which was given the yawn-inducing title “Computational investigation of the social function of domestic cat signals” (in English: using AI to figure out how our house cats “talk” to each other), started with observations of felines playing with each other in cat cafes.
From there, the coders and mathematicians on the team created an algorithm to record and sort the facial expressions the cafe cats used, employing CatFACS (Cat Facial Action Coding System) to associate each expression with its meaning.

Cats make a surprising number of facial expressions, 276 in total, according to a 2023 study.
The problem is, we humans are terrible at reading them. Even veterinarians trained in CatFACS still struggle to get it right, but happily this is precisely the sort of task algorithmic AI excels at. Like facial recognition software, a well-trained machine learning algorithm can recognize faces and record them more accurately and much faster than any person could.
In a column praising the facial expressions study, evolutionary biologist and Jane Goodall Foundation ethics board member Mark Bekoff said it’s the kind of labor-intensive work that truly advances our understanding of the ways animals communicate.
For cats and their human caretakers, Bekoff notes, it could help us reduce inter-species misunderstandings and make it easier to read our cat’s emotions, so we know when they’re not feeling well or need something.
“There are no substitutes for doing what’s needed to learn about the nitty-gritty details of how animals communicate with one another in different contexts,” Bekoff wrote. “This study of play opens the door for more widespread comparative research focusing on how animals talk to one another.”

We also know adult cats very rarely meow to each other, and the meow is reserved for cat-to-human communication. Imagine the frustration our little friends must feel when they have so much to tell us, but the only thing we understand are vocalizations — meows, chirps and trills — that can convey only basic ideas at best.