The Washington Post has a story today about pet cloning, and thankfully it doesn’t sugar-coat the process.
It does take 10 paragraphs for the story to get to the negatives, but it offers a solid explanation of the cloning process before this quote by Columbia University bioethicist Robert Klitzman:
“People think, ‘Oh, I’ll just press a button and out will come Fido,’ but that’s just not the case. So you may love Fido, but do you really want several animals to die and suffer in order to have the one healthy Fido?”
That’s because even with the advancements made in the 21 years since CC the cat became the first of her kind to be cloned, the process still only has a 20 percent success rate. The other 80 percent of attempts end in still births, animals who die shortly after birth due to genetic defects, or animals who survive but suffer from flaws that make them “unsuitable” for the clients who are paying tens of thousands of dollars to clone their cats and dogs.

As we’ve noted before, cloning doesn’t actually guarantee that you’ll get animal who looks like the departed pet. Fur color, length and coat patterns are all variable, and temperament is even more of a crapshoot thanks to the many variables in both nature and nurture.
Klitzman puts it in stark terms.
“I can either pay thousands of dollars to create a new pet that’s actually going to have a different history and personality,” he told the Post. “Or maybe I could adopt an animal that would otherwise be killed in a shelter. Those are things that ethically need to be considered.”
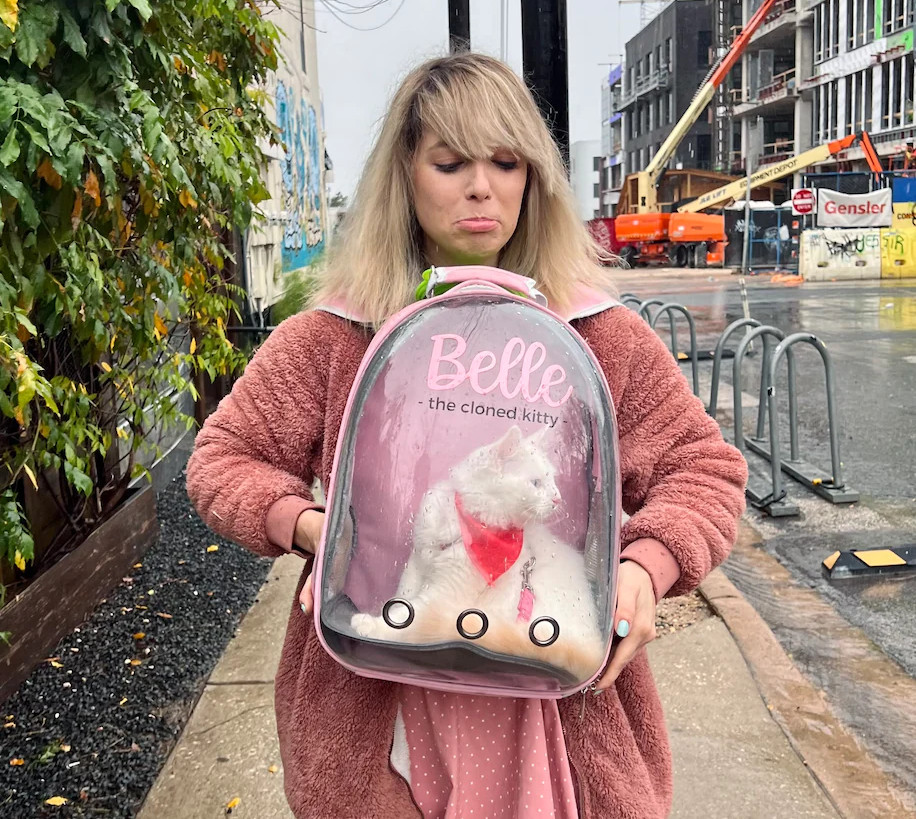
The Post’s article centers on Kelly Anderson and her cat, Belle. If the names sound familiar, that’s because we’ve written about them in earlier posts. Belle was cloned from Anderson’s beloved cat, Chai, and has her looks but not her disposition.
CC was famously different from Rainbow, the cat she was cloned from. While Rainbow had a Calico pattern with tabby stripes on her head, CC had tabby stripes on both her head and her sides. As the BBC noted in 2002, shortly after CC’s birth was announced, the cloned cat’s coat differed from her “mother’s” “because the pattern of colours on multicoloured animals is determined by events in the womb rather than by genes – a reminder that clones may be genetic copies of their parent but are never quite identical.”

John Mendola, a retired NYPD officer from Staten Island, features in a BBC story posted last week on the increasingly popular cloning option.
Mendola paid $50,000 to have his dog, Princess, cloned. It’s not clear how many unsuccessful attempts were involved — and Texas-based Viagen doesn’t reveal that information — but the successful litter produced two dogs who look like Princess, which Mendola named Princess Ariel and Princess Jasmine. (Dude really loves Disney animation, apparently.)
Viagen charges between $25,000 and $35,000 to clone cats, according to different press reports. Grieving pet parents who haven’t made up their minds can have their late pets’ DNA preserved with the company for $1,600. There’s a short window after death during which viable cells can be harvested, but once they’re stored, they can last years or even decades thanks to cryopreservation methods. In one case, a client decided to clone a dog after storing the DNA for 17 years, Viagen’s Melain Rodriguez told the Post.
Viagen doesn’t disclose figures, but the company said it’s cloning more animals — dogs, cats and horses — every year, and has cloned “hundreds” for clients so far.
Blake Russell, the company’s president, likened cloning to a cat or dog having a littermate separated by time.
“A cloned pet is, simply put, an identical genetic twin,” he said, “separated by years, decades, perhaps centuries.”
Animal welfare groups remain staunchly opposed, not only because of the suffering among cloning failures and surrogate mothers, but also because millions of unwanted cats and dogs are euthanized annually.
“Animals’ personalities, quirks, and very essence simply cannot be replicated,” PETA UK Director Elisa Allen told the BBC. “And when you consider that millions of wonderful, adoptable dogs and cats are languishing in animal shelters every year or dying in terrifying ways after being abandoned, you realise that cloning adds to the homeless-animal overpopulation crisis.”