Not only is he the rarest puma in existence, he’s more well-traveled than most humans.
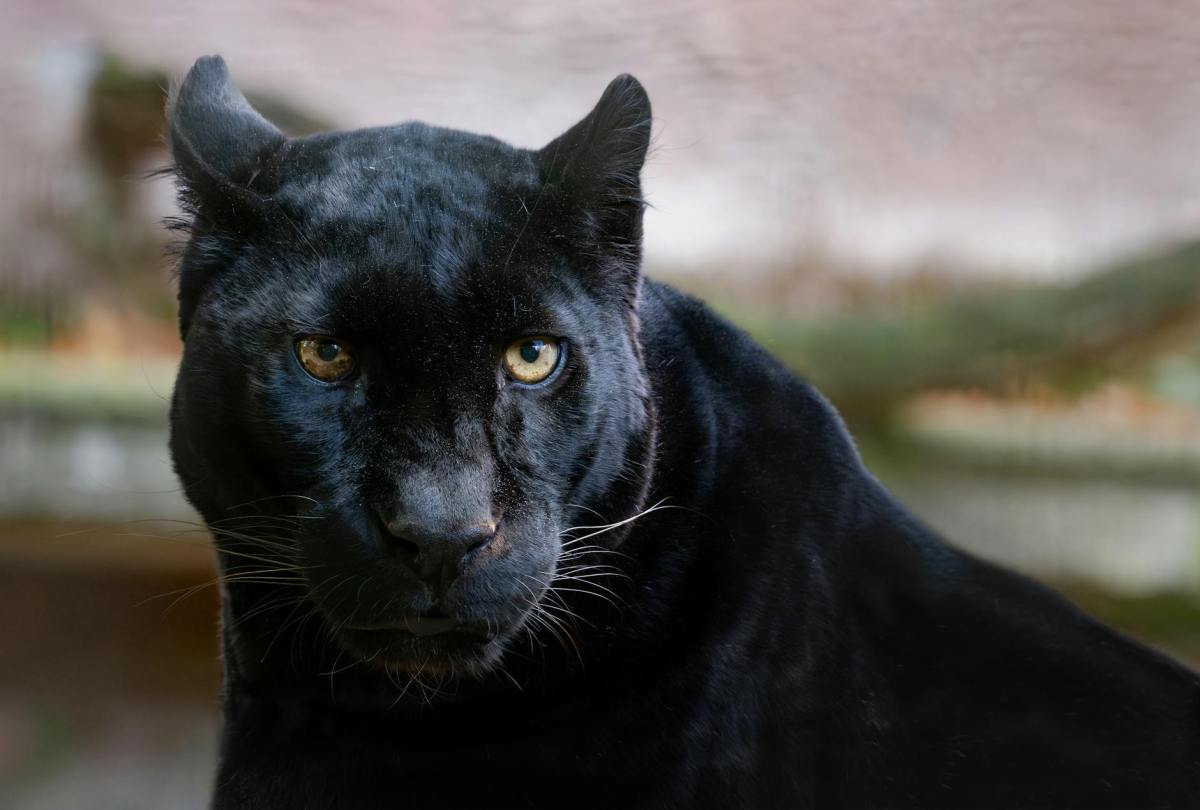
The mountain lion in question has a black coat, unprecedented for his species, and has been popping up all over Facebook. He’s photographed from the passenger seat of a truck cab, his tail in an unbothered curl, crouched amid the brush near a rural road.
Some posters claim they spotted the formidable feline in Mississippi. Others attribute the image to a sister-in-law who lives near Houston or a daughter in Charleston. A user in Louisiana claimed they took the photograph near the bayou, while another places the cat in Wyoming and claims he’s the first-ever documented “shadow cougar.” (Our friend Leah of Catwoods drew our attention to the images last week after seeing posts placing the cat in the south.)



In case it isn’t obvious, all the claims are full of it.
There is no such thing as a melanistic (black) mountain lion, and the big cat in the photo has the physical characteristics of a leopard, an animal that is not native to this hemisphere, let alone this continent.
The real story here is that Facebook remains a fountain of misinformation and Meta (its parent company) doesn’t care. Unscrupulous users will do anything to get attention and the clicks that come with it, and the average Facebook user is happy to indulge them, driving clicks by resharing the hoax content and juicing its algorithmic value by engaging in endless arguments with fellow users about the veracity and provenance of the photos.
Alleged big cat sightings are perfect for this sort of thing because they pique people’s natural curiosity, there’s a whiff of danger — especially when the poster claims the animal was spotted locally — and most people aren’t aware of telltale differences between cat species.
In many ways, the blurrier and more indeterminate the photo, the better: like Bigfoot and the Loch Ness monster, the idea of phantom cats is most fertile in the imagination.
These days you don’t even need a photo to get in on the click-baiting action. I asked Gemini to create an image of a jaguar-like big cat walking along a rural road at night, and this is what the LLM gave me:

In the image prompt, I asked it to make it look like an amateur photo taken with a midrange smartphone camera, but if we really wanted to get artistic, it’s simple enough to add noise, maybe some motion blur and digital artefacts to the image to make it look more like an authentically crappy, rushed shot of an unexpected animal.
Here’s the result of some simple efforts to en-crapify the “photo” further:

To give the image urgency and encourage people to engage with it, I can make it local and claim it was recent. Errors of grammar, spelling and punctuation add a nice seasoning of authenticity, along for feigned concern for others as the reason for sharing:
“Folks – just wanted to tell ya’ll to mind your pets an make sure of you’re surroundings bc theres a big cat on the lose!! my cousins GF took thus friday nite on Route 9 a few mile’s south of Dennies. a real honest to goodness black panther! BE SAFE!!!”
There’s a dangerous animal on the loose in your area! You know what you have to do: share it so others can bring their pets safely inside and stop their kids from playing outdoors, at least until it looks like the predator has moved on.
It’s your duty as a good American!
Since it doesn’t seem to matter if a quick reverse image search can settle the question of where an image came from, it’ll be interesting to see if anyone lifts the above image and text.
At the very least, maybe a few people who do think to run a search will find their way here, read about the hoax, and save themselves from getting drawn into online debates about the existence of cryptid cats.