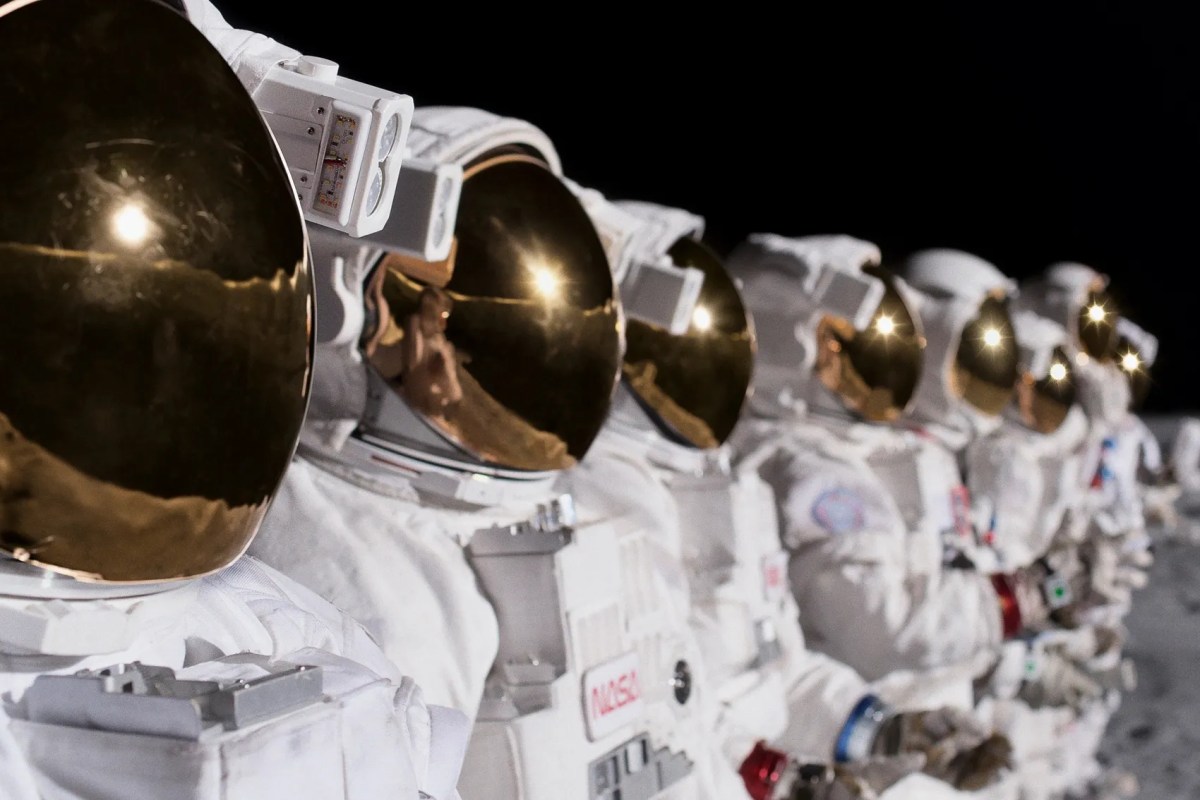
The first few minutes of For All Mankind play out like a documentary for the Apollo moon landing, interspersing archival footage of tense staff in mission control with shots of engineers in horn-rimmed glasses poring over data, backup astronauts raising their glasses in a pub and nervous families sitting in their 1960s living rooms, crowding around televisions.
A news anchor cuts in to report he’s getting the live feed from the moon. We see the door of a lander open…and a Soviet cosmonaut strides out, planting the flag of the USSR on the lunar surface and becoming the first human to ever set foot on another world.
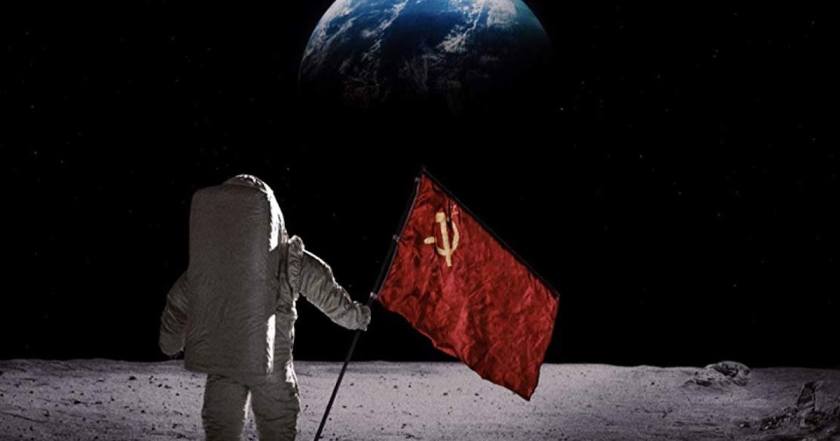

That’s the premise of For All Mankind. In this alternate history series, the fire that killed astronauts Virgil Grissom, Edward White and Roger Chaffee on Apollo I’s launchpad — which indeed happened in real life — led to policy changes and a more cautious culture at America’s space agency, resulting in the US losing the first and most momentous achievement of the space race.
That’s the start of the what-ifs.
What if the Soviets beat us to the moon? What if the rest of the space race was even more competitive than it was in our history, with an America struggling to prove its primacy? What if the US and Soviet Russia continued to pour incredible resources into space exploration? How far would we go? What kind of incredible new technologies would we invent? How would all of it impact American politics, culture, identity and standing in the world?
Could it have led to a better future?
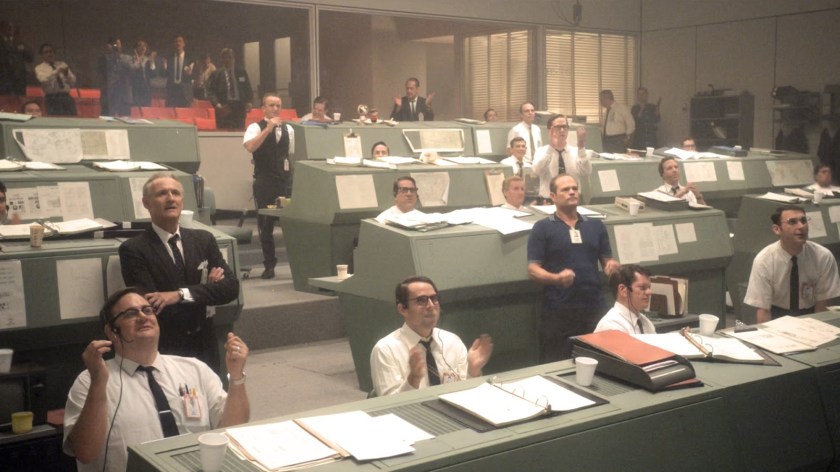

The answer to that question is hinted at in the series’ title, and while the show is filled with tense moments of international, organizational and personal rivalry, it’s infused with rational optimism instead of the cheesy, manufactured aspiration we’re accustomed to. It’s more like asking: What could the human race achieve if we all worked together? Is that retrofuturistic gleaming vision of the future still possible, and how do we get there?
For All Mankind follows Ed Baldwin (Joel Kinnaman) and Gordo Stevens (Michael Dorman), astronauts and best friends whose Apollo mission came within a few thousand feet of landing on the moon just weeks before the Russian landing.
They’re miserable as they sit in a dive bar just off NASA’s campus watching grainy footage of cosmonauts claim their glory, and blame themselves for their failure to land even though it wasn’t in NASA’s cautious mission plan.

The scenes that follow look like they could have come from the 1995 blockbuster Apollo 13 as we meet the astronauts, their kids and their nervous wives, the eggheads and flight directors at NASA, and the political players who keep the space agency funded and protected from the wrath of President Richard Nixon.
With the agency rocked by the Soviet achievement and intense political pressure, it embarks on a series of bold new endeavors dictated by the White House. Not only will Americans land on the moon, they will build a permanent base there, and — embarrassed and spurred on by the fact that one of the cosmonauts was female — NASA will for the first time train a new, all-female class of astronaut recruits.
The later group includes hotshot pilot Molly Cobb, “token black girl” Danielle Poole, quiet but determined Ellen Waverly — and Tracy Stevens, astronaut Gordo Stevens’ beautiful wife who is an accomplished pilot in her own right. While the women manage the normal pressure that comes with astronaut training and the high stakes nature of the job, they must also contend with pushback coming from directions they don’t expect — including hostility from some of the wives of current astronauts, who feel their husbands’ jobs will be threatened by women in space.
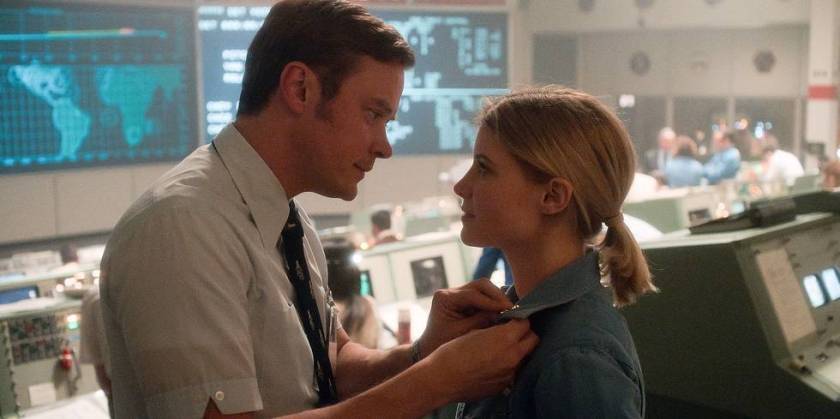


For All Mankind is a science fiction show, but it’s also a drama and a thriller, putting viewers through the wringer of emotions.
There are funny and amusing moments as the show references celebrities, political figures and musicians from the 1960s onward, grounding the narrative in American culture. The fortunes of some celebrities and politicians change in the show’s alternate history while others stay the same.
In one running storyline — which you’ll only catch if you pay close attention to certain scenes and montages — John Lennon survives the attempt on his life, continues on as the grating, post-Beatles John Lennon most people would like to forget, and becomes just another aging musician cashing in on past glory alongside bandmate Paul McCartney and bands like the Rolling Stones.
The extension of the space race and continuation of US-Soviet rivalry impacts society in profound ways, many of them we may not realize from our historical perspective.
For example, DARPA created the internet because the US government and military wanted a decentralized communications network that could withstand nuclear attacks and remain operational even if major nodes are taken out in nuclear blasts.
That’s why the internet works on such a wide variety of hardware and why, even when major servers go down, our routers are able to move data packets via alternate paths. It’s difficult to imagine a time when the web wasn’t a medium for exchanging photos and videos of cute cats, but the early internet was populated by government officials, Pentagon brass and leading scientists in crucial fields.
In real life, restrictions were taken off the internet when the Soviet threat began to fade, allowing widespread civilian adoption of the technology and early dial-up services like AOL and CompuServe.
That doesn’t happen in For All Mankind’s alternate history as the USSR and communism remains a major threat, resulting in pop culture developing along a different cultural arc than the one we’re accustomed to.
While the pop culture references, sets, cars and costumes help ground For All Mankind historically, the show is at its best when it puts us in mission control and the command modules of high-risk space missions, constantly reminding us of the danger these men and women face while highlighting the commonality of astronauts, cosmonauts and later space explorers from other countries, all of them just human beings millions of miles from their families and everything they’ve ever known.
At the same time, the US and the USSR are playing a game of nuclear brinkmanship and astronauts are in many ways on the front lines as they figure out how to co-exist in unprecedented circumstances and places famously inhospitable to human life.
If astronauts tap a lunar mine too close to Soviet base camp, could that start a war? Are the Soviets spying on communications between NASA and its astronauts on the moon? What happens if someone gets hurt and their blood can’t clot in low/zero gravity?
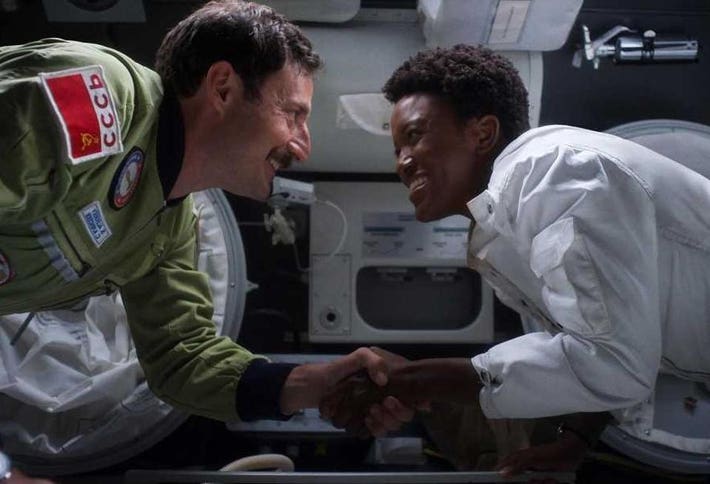

Kinnaman, Dorman, Sarah Jones (Tracy Stevens), Sonya Walger (Cobb) et al shine in those scenes as they juggle the pressure of surviving in space with being exemplars of — and diplomats for — their country. Rather than be content painting the Soviets as the traditional bad guys, the show also gives us a close-up look at the people in the USSR’s space program and the pressures they face, particularly Polish actor Piotr Aleksander Adamczyk’s Sergei Nikulov in his relationship with his NASA counterpart, flight director Margo Madison.
In one of the show’s quieter moments, Poole (Krys Marshall) takes two cosmonauts to The Outpost when, during joint training exercises, they request real American cheeseburgers and whiskey. After a few drinks one of the cosmonauts grows somber and tells Poole how he held Laika, the Moscow street dog who was famously blasted into low Earth orbit in her own little module, before scientists were sure enough in the technology to risk human lives.
Although Soviet propaganda feted Laika as a hero and the official story said she survived until re-entry, the cosmonaut tells Poole that Laika died shortly after liftoff, terrified, alone and subjected to unimaginable forces as thousands of pounds of fuel carried her capsule heavenward via brute force.
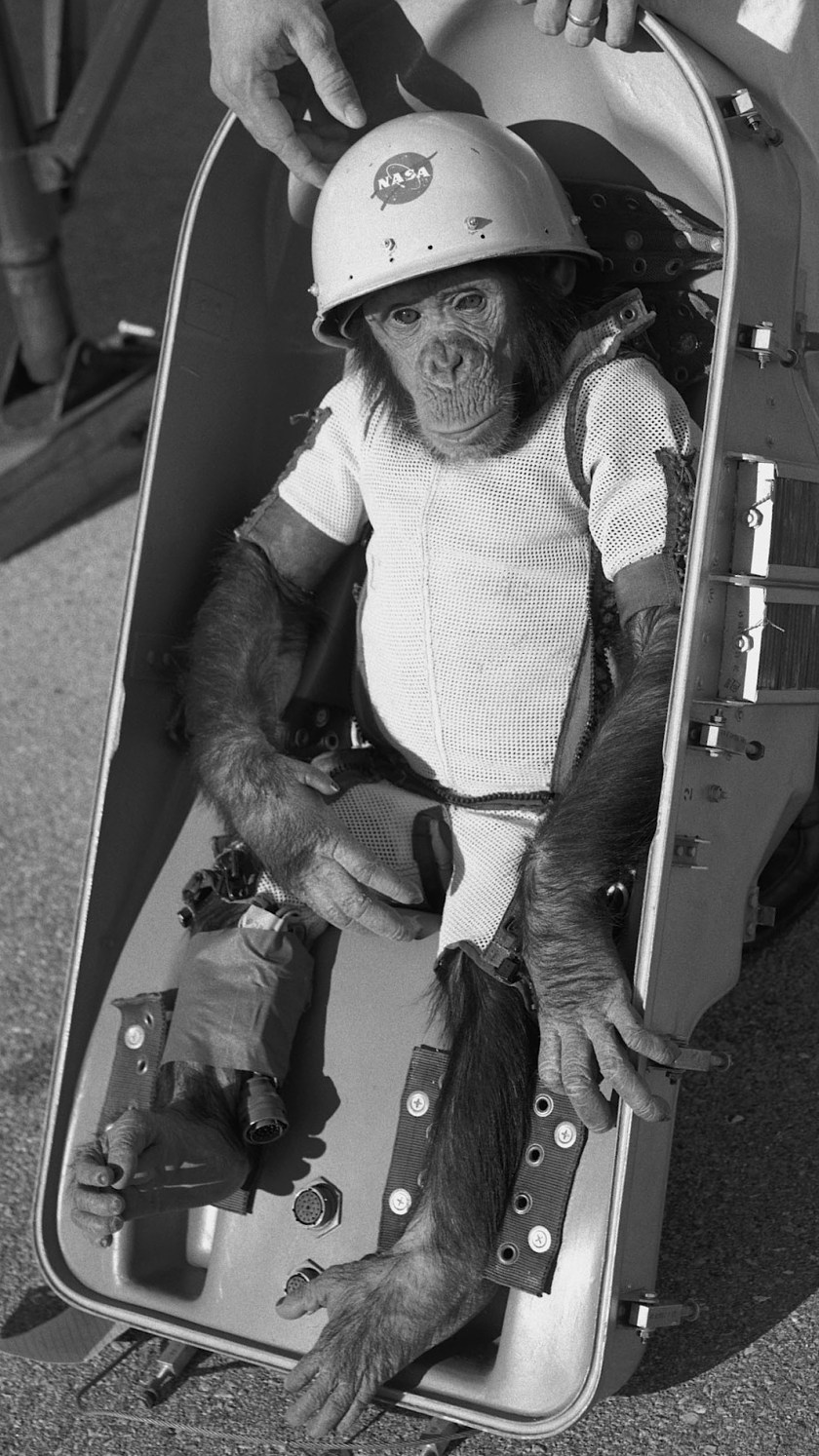
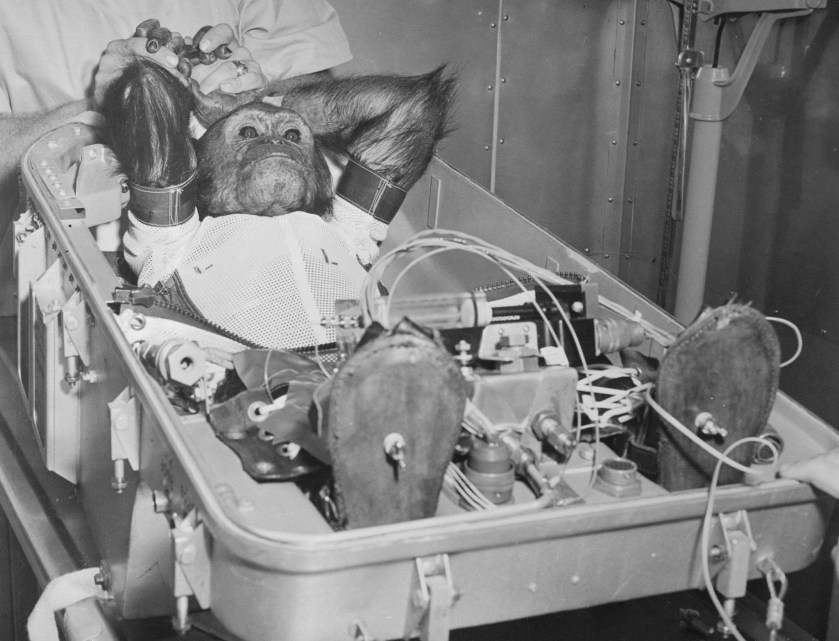
(The west was no less barbaric: The French famously sent a street cat named Felicette into space while NASA used a young chimp named Ham. In all of those cases the animals were named only after their missions, as mission commanders didn’t want to risk humanizing them in the event of disaster. Had Felicette and Ham both died in space they’d be remembered only by their identification numbers as footnotes in early space history.)
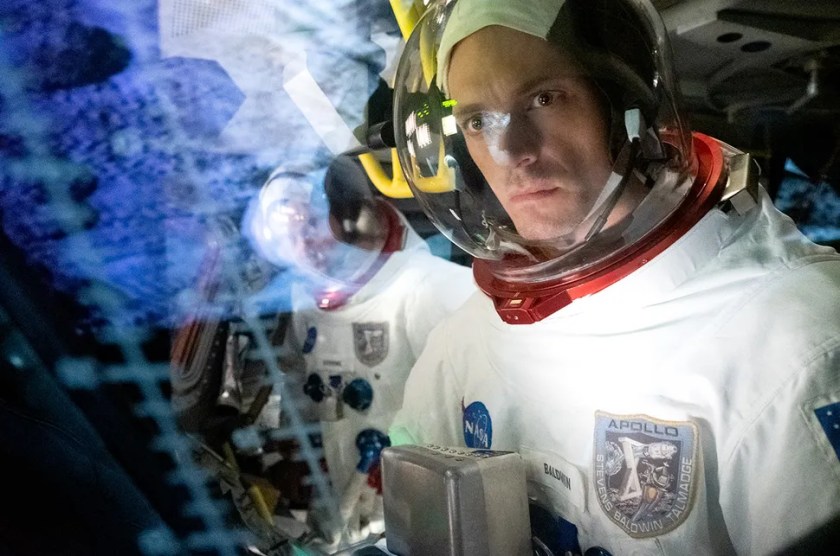

For All Mankind recently began its fourth season and because AppleTV’s marketing and promotion is curiously weak, it remains one of TV’s best-kept secrets. If you haven’t seen the show yet, now’s a great time to jump aboard with so many TV shows on hiatus for the holidays and many others pushed back or canceled in the wake of the parallel strikes that halted production for most of 2023.
For All Mankind
Network: Apple TV
Content rating: TV-MA for bad language, occasional drug and alcohol use and mature themes.
Ratings: 8.1 (IMDB), 93% (Rotten Tomatoes), 4/5 (Common Sense Media)
Seasons: 4 (current)
PITB verdict: 4 Paws!