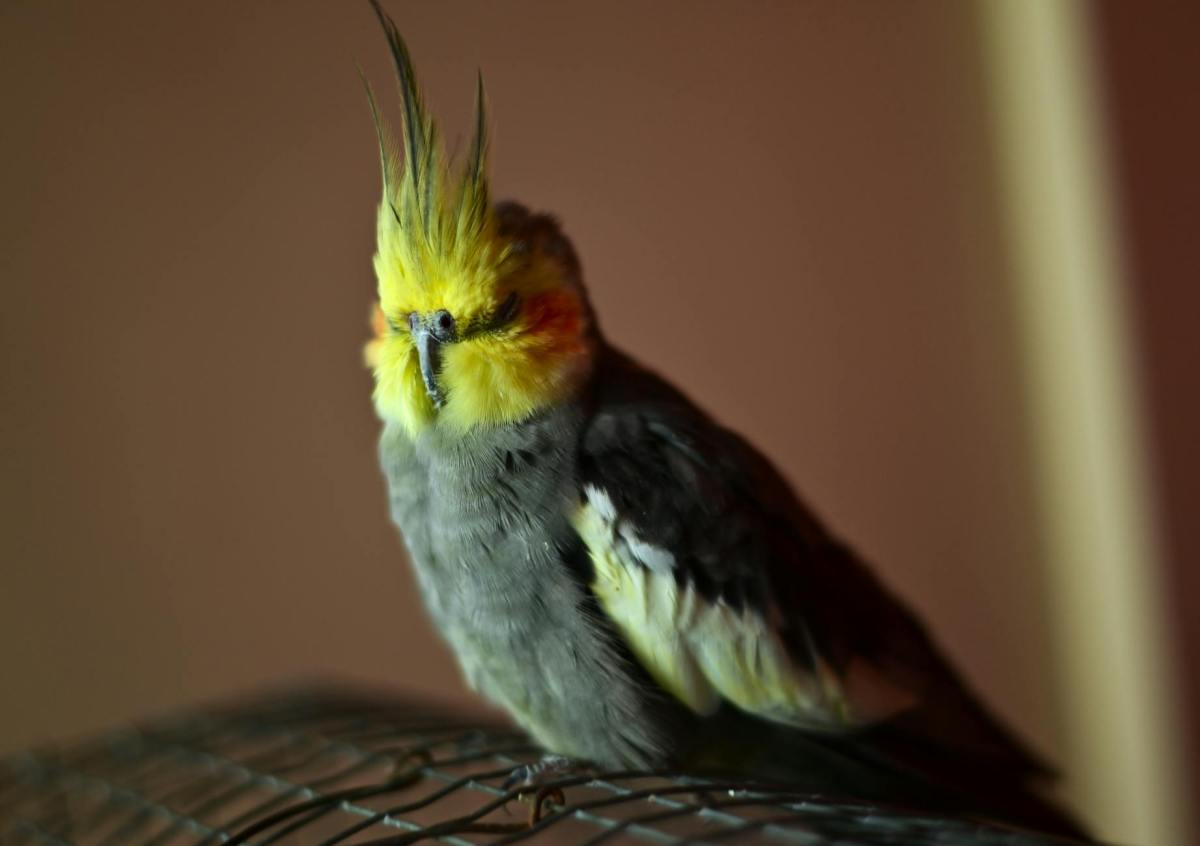
Meet Kiki the cockatiel, a bird who loves Earth, Wind and Fire so much that he sings the band’s classic hit, September, regularly — whether he’s just chilling by himself, singing along to the recording or driving his human crazy by whistling the catchy hook at ungodly hours.
“Kiki, it’s seven in the morning!” she tells him in one clip, raising an admonishing finger. “Silence!”
Kiki regards her for moment as if her request is absurd, then launches right back into September.
Hey, hey, hey
Ba-dee-ya, say, do you remember?
Ba-dee-ya, dancin’ in September
Ba-dee-ya, never was a cloudy day
In another video Kiki’s human sets her phone to record and leaves the room, and Kiki busts out his favorite song again. He’s got great taste in music!
I’ve always thought parrots are a fascinating example of animal cognition and further proof that we share our planet with billions of other minds who think and feel.
Humans and birds last shared a common ancestor more than 300 million years ago. That means between them there’s been more than 600 million years of divergent evolution resulting in radically different physiology, abilities and minds.
Yet parrots can speak while non-human primates (apes and monkeys) cannot!
For decades scientists thought apes and monkeys, by virtue of their relative similarity to humans, possessed an inmate affinity for language and that the physical limits of their vocal apparatus is what keeps them from speaking.
But a 2016 study by a team from Princeton University found monkeys do possess the vocal “hardware” to speak, meaning their mouths and throats are capable of making the sounds necessary for human language. It’s the lack of associated brain circuitry that prevents them from talking.
If the ability to speak and the ability to dance/appreciate music and rhythm is uniquely human among the primate order, and birds arrived at it at a different point in their evolutionary history, that means language and appreciation for music/rhythm developed separately along two divergent evolutionary lines!
That’s incredible and has intriguing implications for the cognitive abilities of animals.
A common argument is that birds with the ability to form human speech are simply mimicking sounds and don’t understand what they’re saying. That’s a natural assumption given what we think we know about non-human capacity for understanding language, but research suggests it’s wrong.
Take a look at this video of the famous late African grey parrot, Alex:
When Dr. Irene Pepperberg asks Alex how many blue blocks are present on a tray with a random assortment of blocks, balls and triangular toys in different colors, Alex can’t give a rote answer. First he has to understand that a question is a request for information and not part of the strange human ritual called small talk. He can’t simply count or guess at the number of blocks either.
Instead, Alex has to perform two calculations. He must tally the blue objects and count the number of them that are blocks, or he’s got to count the number of blocks and figure out how many of them are blue.
If he was simply repeating information in context — like saying “Hello!” when a person walks into a room — Alex wouldn’t be able to correctly answer the questions, and Pepperberg’s research funding would have dried up. Instead, Alex became a focal point of research that persisted for decades.
There’s no indication Alex could master syntax, which has proven elusive for even the smartest animals. But the African grey, who died in 2007 at 31 years old, was curious, asking questions that were unique and unexpected of an animal. He once asked his caretakers to describe his physical appearance, and the night before he died, he told Pepperberg: “You be good. I love you. See you tomorrow.”
We’ve talked about parrots before on PITB, including Snowball the dancing cockatiel who not only appreciates music and has a great sense of rhythm, but also has an entire repertoire of unique dance moves. Then there’s my personal favorite, Ruby the African grey, who has demonstrated mastery of absolutely vile, uniquely British insults.
Sure, there may not be much research value in hearing Ruby hurl verbal abuse at her very loving human, Nick Chapman, but few things have made me laugh as hard as that extraordinarily foul-mouthed bird. She has to be seen and heard to be believed. (But if you’ve got kids in the room, stick with the wholesome Snowball. He’s got serious moves.)

Now if you’ll excuse me, I’m off to teach a certain feline a few Earth, Wind and Fire songs in the hope that he’ll give up on the screeching meows and use his natural falsetto for a more gentle wake-up experience.
Hey, hey, hey
Ba-dee-ya, hey there my Big Buddy
Ba-dee-ya, Little Buddy’s hungry!
Ba-dee-ya, get your lazy ass up and feeeeeed me!