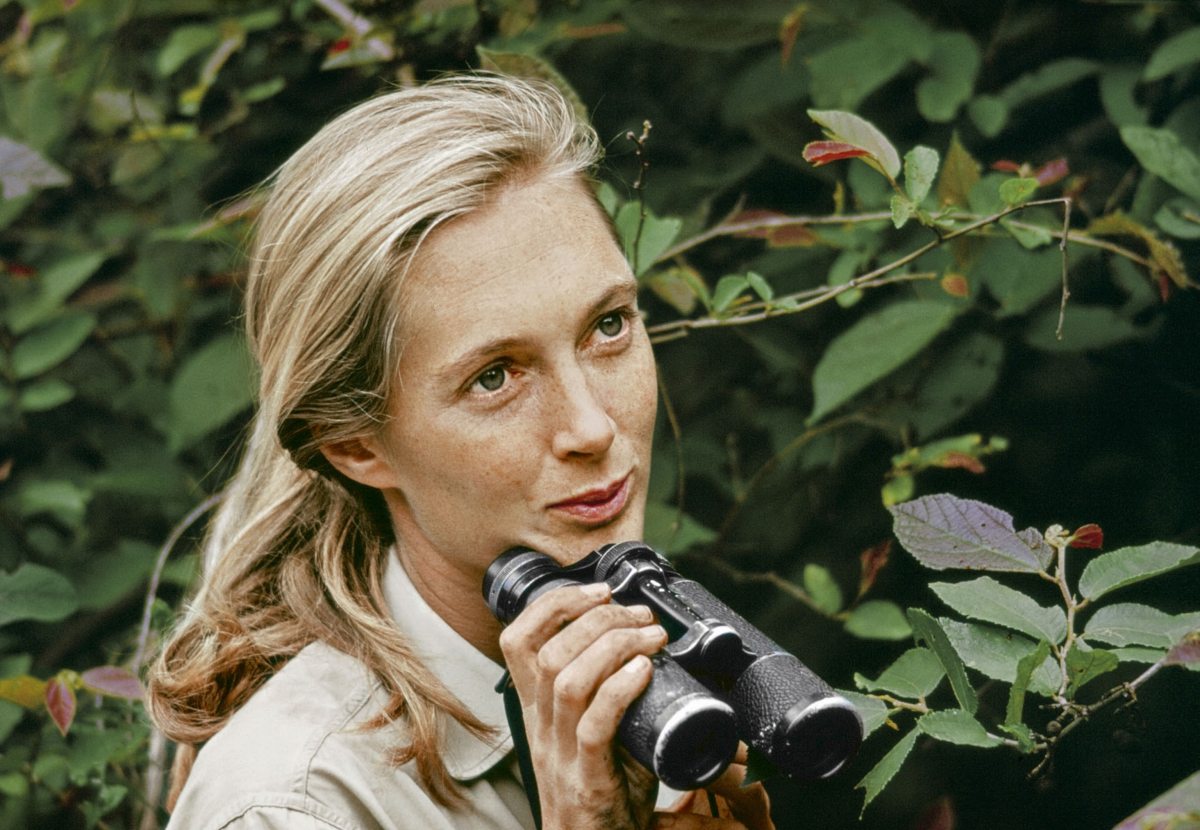
As I’m sure most of you have heard, Jane Goodall passed away Wednesday of natural causes. She was 91.
Goodall’s work was revolutionary and her career was extraordinary. It’s difficult to imagine now, but when Goodall first pitched camp in Tanzania’s Gombe Stream National Park in July of 1960, the scientific community knew virtually nothing about great apes.
Goodall wasn’t exactly welcomed with open arms. Being female and photogenic were the first two strikes against her in the eyes of the establishment.
She was self-taught, didn’t have a degree (she later earned a doctorate at Cambridge), and perhaps her biggest “sins” involved empathy and an attitude more buttoned-up scientists saw as anthropomorphizing the animals.

Goodall gave the chimps names (a no-no at the time among scientists), carefully observed and recorded their family trees, worked out the obtuse — to human eyes– social hierarchy of primate troops, and witnessed behavior that no one had ever seen before.
She saw friendship, love and loyalty among the chimpanzees, witnessed a bitter war between the Gombe troop and a splinter group, followed families over generations, and saw one chimp die of a broken heart after his mother passed away. (I recommend Goodall’s 1990 book, Through A Window: Thirty Years With The Chimpanzees of Gombe, and the 2002 follow-up, My Life With Chimpanzees, for anyone who wants to read more.)
Her first major contribution, in October of 1960, not only fundamentally challenged our assumptions about animals, it forced us to change the way we regard our own species.
Goodall, observing the chimpanzees from a distance despite the rain that day, watched as a male she named David Graybeard repeatedly dipped blades of grass into the Earth. Curious, Goodall approached the site after Graybeard left, grabbed a few blades of grass and imitated what she’d seen the chimp doing.
She was astonished when she pulled the grass out and the strands were covered in termites. David Graybeard had been eating. He was using a tool to eat!

The discovery was huge because scientists believed tool use was, at the time, limited to mankind. We build and use tools, animals don’t, the thinking went.
When Goodall reported her findings to her mentor, anthropologist Louis Leakey, his prompt response indicated the gravity of her discovery: “Now we must redefine ‘tool,’ redefine ‘man,’ or accept chimpanzees as humans.”
Goodall never stopped working with the chimpanzees of Gombe, and today her formerly humble camp has become a permanent compound where researchers — all inspired by Goodall’s story — continue to study our genetic relatives.
But in her later years, Goodall became known for her activism just as much as her work as a scientist. She traveled constantly, engaging audiences on the subjects of animal conservation, respect for nature and understanding our place in the natural order. It’s a job that has become more necessary than ever as relentless human expansion, habitat fragmentation and human behavior push thousands of species toward extinction.

We lost Frans de Waal, the famous primatologist, in 2024. Now we’ve lost Goodall, and Sir David Attenborough is less than six months shy of his 100th birthday. We’re going to need people to pick up where they left off, and the job is much more difficult than it looks, requiring expertise, charisma and the ability to connect with audiences who know little about the subject matter.
But that’s a problem for another time. For now, let’s remember Jane and appreciate all she’s done over the span of an incredible life and career.